» Introduction
Updated on 2019-03-09: Using go mod instead of dep.
I’ve created a very minimalistc repository to show, how to deploy Go code to Heroku using GitLab CI.
Automatically triggered on push/merge:
- golint
- go tool vet
- go test -race
- deploy to staging (automatically)
- deploy to production (manually)
» How-To
Create a new Heroku Pipeline.
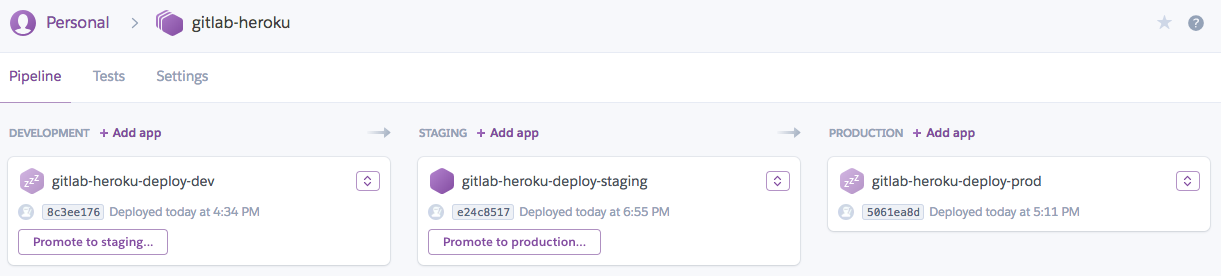
Set up as many Heroku apps in this pipeline as you need (e.g. staging and production).
git clonethis repository or copy whatever you need.Get your Heroku API key found in your account.
Set the key as the variable
HEROKU_API_KEYin your GitLab CI / CD Settings.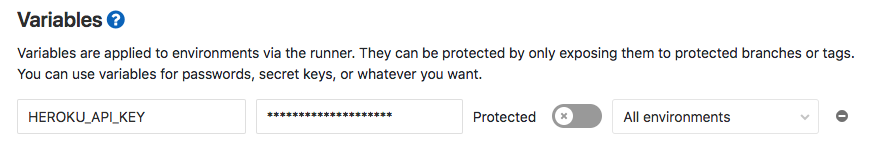
Modify
.gitlab-ci.ymland change the existing app name (-app=gitlab-heroku-deploy-*) to your newly created apps.
» Hints
Heroku uses the $PORT environment variable (see
main.go)In this setup, Heroku knows what to deploy based on the modified
go.modfile (see buildpack for alternatives):1// +heroku install .This is not required here, and
.is the default, but when your main file is in a different folder, you have to give the corresponding path instead of the..The
Procfiledecides which command should be run. Again, in this setup it’s not required as the binary is the same as the project name. When you have to run another command, change the command afterweb:accordingly (The Procfile).1web: go-heroku
» Older approach using godep
See the using-godep branch for an example using dep instead of go modules.
» Further Reading
- Inspired by Stacy Goh: Setting up CI/CD on Gitlab (using node)
- GitLab CI/CD Examples
- Also inspiring and more complete, using a Makefile but without Heroku: Go tools and GitLab: How to do continuous integration like a boss